Deadly outbreak of Marburg, or ‘bleeding eye virus,’ leads to travel advisory
Health officials continue to monitor an outbreak of Marburg virus — also known as "bleeding eye virus" — in Rwanda, which has sparked concerns about a potential spread outside the country.
The U.S. State Department issued a travel advisory on Nov. 22, recommending that travelers exercise "increased caution" in Rwanda due to the outbreak.
"Travelers may be subject to additional health screenings [when] entering and exiting Rwanda," the advisory stated.
BIRD FLU SURGES IN SEVERAL US STATES WITH REPORTS OF NEW OUTBREAKS: 'GETTING WORSE'
What is Marburg virus?
Similar to the Elbola virus, Marburg is a "rare but severe viral hemorrhagic fever" that is highly deadly, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). It has a 20% to 90% fatality rate.
The first case in Rwanda was confirmed in September. As of Nov. 29, the country had reported 66 cases of the virus and 15 deaths. Most of the infected people have been health care workers.
Approximately 75% of the patients with Marburg have recovered, according to the CDC.
There have not been any confirmed cases in the United States, and the CDC says the risk of infection in the country is low.
LEGIONNAIRES’ DISEASE OUTBREAK LINKED TO CRUISE SHIP HOT TUBS, CDC SAYS
"Marburg is one of the deadliest viruses that infect humans," Dr. Marc Siegel, senior medical analyst for Fox News and clinical professor of medicine at NYU Langone Medical Center, told Fox News Digital.
"It is very similar to Ebola in that it causes hemorrhagic fever."
Symptoms of the virus
Initial symptoms usually mimic the flu, including fever, body aches, diarrhea, abdominal pain and vomiting.
The interval between infection and symptoms is typically two to 21 days, according to Siegel.
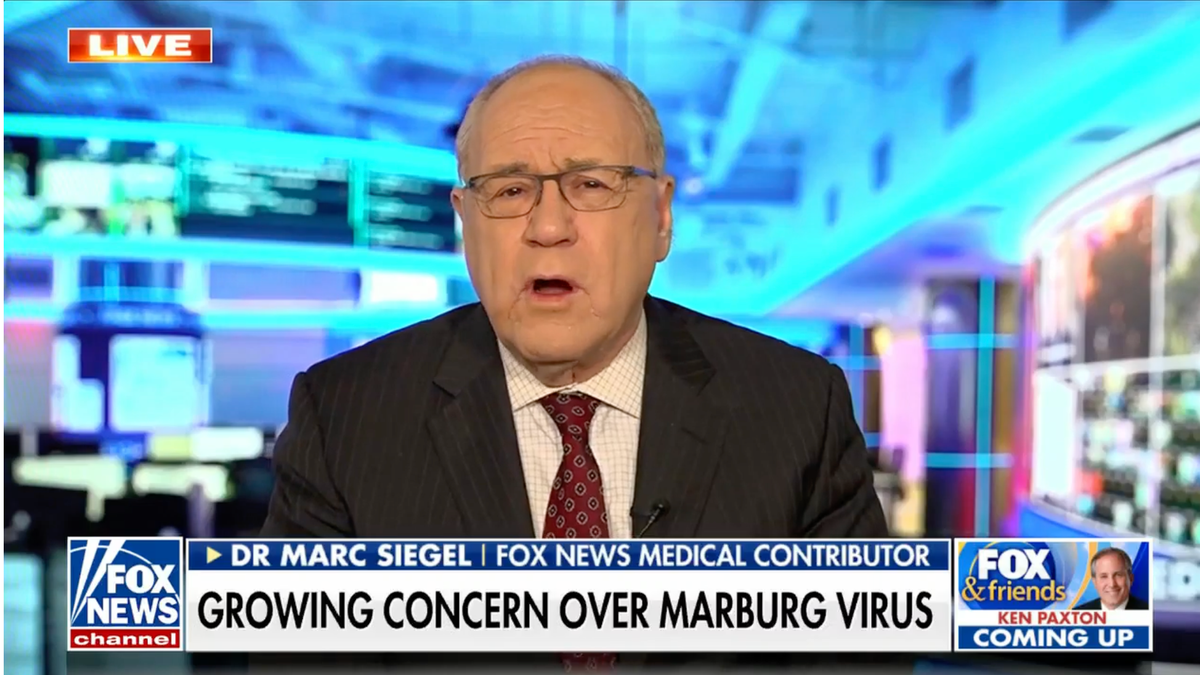
In severe cases, patients may experience extreme weight loss, jaundice, inflammation of the pancreas, delirium, shock, liver failure, massive hemorrhaging and multi-organ dysfunction, the CDC stated.
It can also cause bleeding from the eyes, nose, mouth or gastrointestinal tract, hence the nickname "bleeding eye virus."
The virus is transmitted via bodily surfaces, blood and contact with contaminated surfaces, according to Siegel.
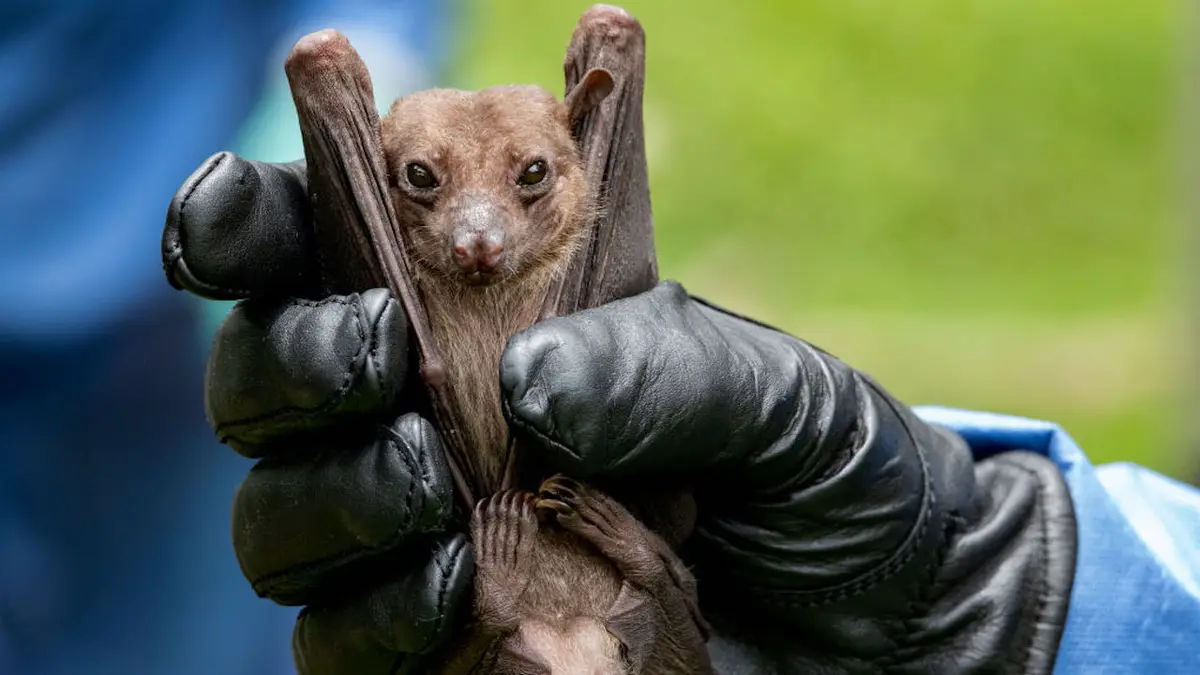
The "primary reservoir" (natural host) for the virus is the Egyptian rousette bat (Rousettus aegyptiacus), the CDC noted.

"There are no adequate drugs or vaccines for Marburg," Siegel told Fox News Digital.
Medical providers can manage symptoms with supportive care, including oxygen, pain medications and IV fluids for rehydration.
"There are other treatments in the works, including an experimental vaccine," the doctor noted.
TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
For those who succumb to the disease, death usually occurs within eight to nine days after symptom onset, Siegel said — typically due to blood loss.
Although the doctor said there is a risk of intercontinental spread, he does not believe it is contagious enough for a widespread outbreak.
Prevention of Marburg
To avoid contracting the virus, the CDC has issued the following recommendations on its website.
- Avoid contact with the blood and bodily fluids of those who are experiencing symptoms.
- Do not touch items that may have come in contact with the bodily fluids of an infected person.
- Avoid contact with Egyptian rousette bats and non-human primates in areas where Marburg cases have been reported.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health
In order for a Marburg outbreak to be officially over, there must be a period of 42 days without any new infections after the last recovered patient has had two negative tests 48 hours apart, according to the CDC.